Acid etching is a process where a hard metal is cut using a specially formulated acid to allow the formation of the desired design onto the metal. The acid etching process uses mordant acids that are available together with chemical compounds to impart a physical or aesthetic improvement to the metal surface. Read More…
The MET Manufacturing Group, LLC process offers many technical & financial advantages in manufacturing various flat metal components. Try this precision etching, non-mechanical process for competitively priced, burr & stress free sheet metal products, up to 62 mil (.062”) thick. Our photo-chemical machining process is also known as photo-fabrication, photo etching, chemical milling & acid...
Etchit is your high-quality solution for custom-manufactured precision metal parts and components. We use photochemical machining to make products for such industries as aerospace, audio, automotive, computer, circuit board, decorative and fastener. Does your product need photo etching processes?

VACCO is the industry leader of Photo Chemical Etching of metal & polyimide components and devices. We specialize in Stainless steel, Titanium, and Copper, but work with a variety of different materials. We have over 60 years of experience in Chem Etching, and we offer Micro Laser Cutting & Welding, and Diffusion & Adhesive Bonding services along with an extensive range of value-added services. ...

Great Lakes Engineering is a trend setting manufacturer of surface mount stencils, precision laser cut parts, and photo chemical etched parts. We work with a wide range of materials, including Stainless Steel, Copper, Titanium, Nitinol, Nickel, Kovar and many others.

More Acid Etching Companies

Acids Used in Acid Etching
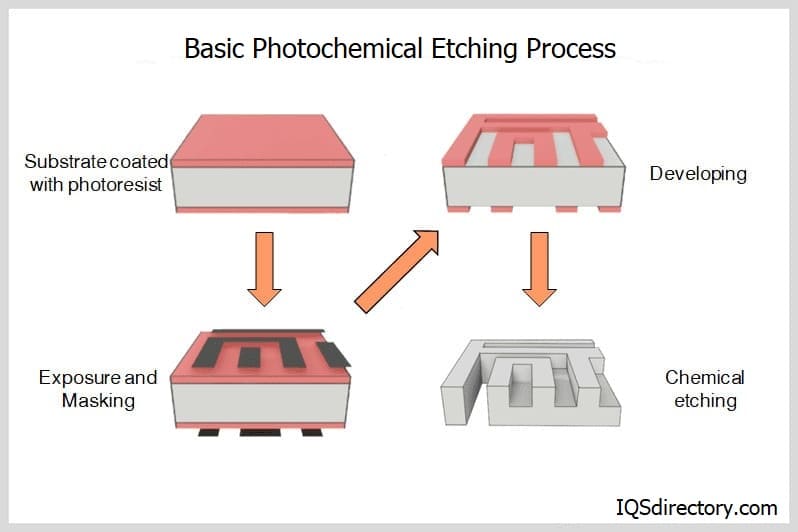
Acid etching, also known as chemical etching or photo etching, is a subtractive manufacturing process that utilizes strong acids to selectively remove material from metal surfaces. This method is widely favored for creating intricate designs, precision components, and fine features in metals. Understanding the different acids used for etching is essential both for safety and for achieving precise results.
Common acids used in the etching of stainless steel and other metals include sulphuric acid and nitric acid. These high-strength acids must be handled with extreme care, as they can dissolve not only metal but also organic materials such as human skin. The concentration and type of acid directly impact the etching speed and the quality of the finished product—a higher acid strength typically equates to a faster etch.

Hydrochloric acid is frequently used in copper etching processes due to its effectiveness in dissolving copper and its alloys. For etching mild steels, copper sulfate serves as a popular mordant. Nitric acid is often diluted, using a one-to-three ratio with distilled water to achieve controlled etching rates while minimizing excessive reactivity.
Other chemical etchants, such as ferric chloride, are widely used in industrial etching applications because of their effectiveness and relatively safer handling compared to mineral acids. Selecting the right etchant is crucial for achieving the desired surface finish, maintaining dimensional accuracy, and ensuring consistent results in high-volume production scenarios.
Metals That Can Be Acid Etched
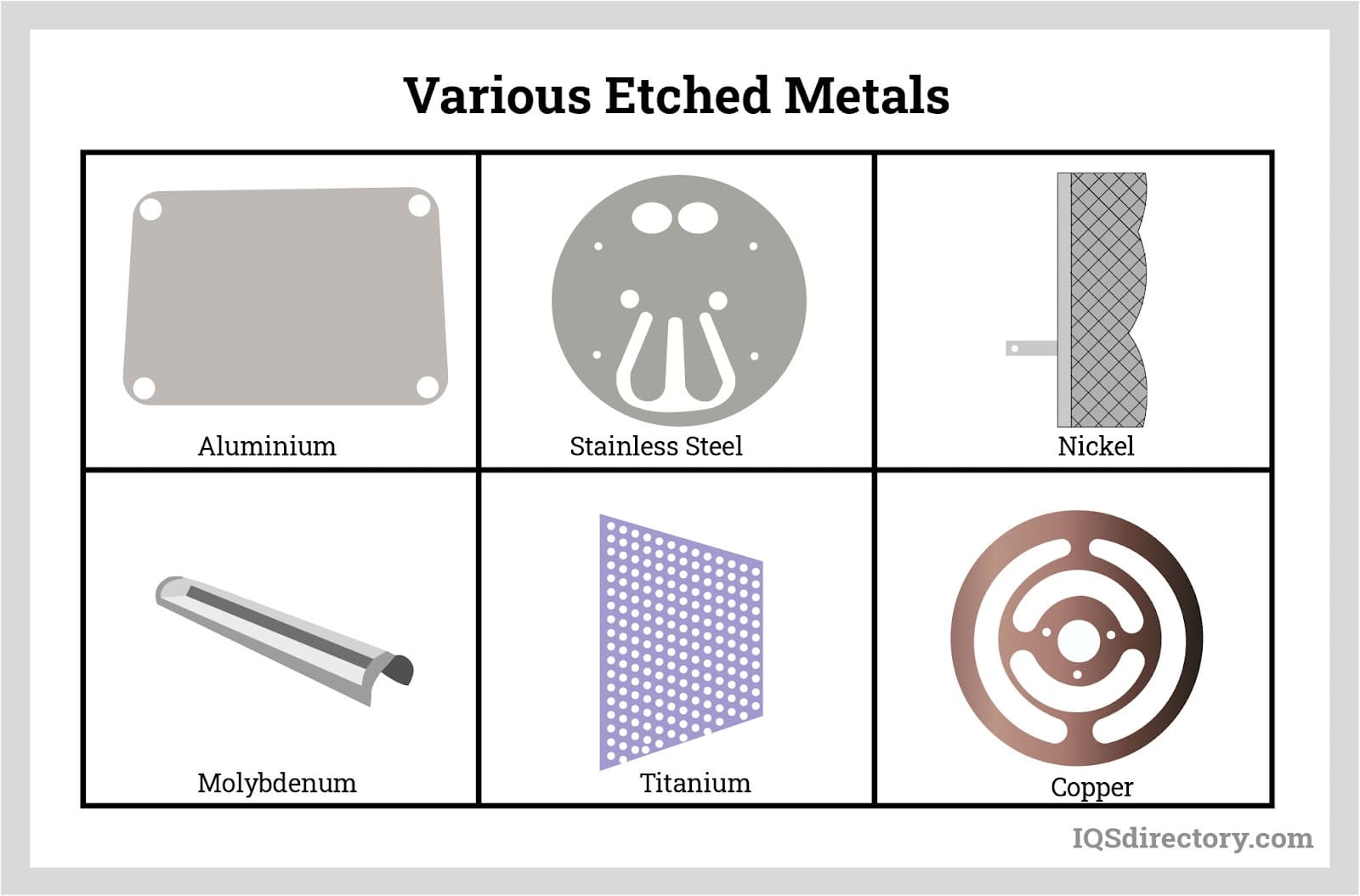
Virtually all metals can be etched using acid, but some are preferred due to their unique properties, compatibility with etchants, and suitability for specific applications. The most commonly etched metals include:

- Titanium – Noted for its strength-to-weight ratio and excellent fatigue resistance, titanium is often acid etched for aerospace, medical, and high-performance engineering applications.
- Aluminum – With its lightweight structure and natural corrosion resistance, aluminum is widely etched to produce decorative finishes, nameplates, and precision parts for automotive and electronics industries.
- Copper – Known for its softness and rapid etching rate, copper is commonly used in the manufacture of printed circuit boards (PCBs), electrical contacts, and intricate decorative elements.
- Nickel – With robust temperature and corrosion resistance, nickel and its alloys are etched for use in chemical processing equipment, battery components, and micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS).
- Stainless Steel – Renowned for its corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, stainless steel is acid etched to create medical devices, filtration screens, and industrial components.
- Bronze – This ductile and hard metal outperforms copper in stiffness, making it ideal for durable etched parts in art, architecture, and industrial products.
- Molybdenum – With high strength, excellent thermal properties, and superior electrical conductivity, molybdenum is etched for use in electronics, lighting, and aerospace sectors.

Other etchable metals include brass, silver, gold, and specialty alloys, each selected based on factors such as conductivity, cost, and compatibility with specific acid solutions. Are you curious about which metals are best for your unique acid etching project? Compare material properties and typical uses to determine the ideal metal for your application.
Types of Acid Etchings
Acid etching processes can be tailored to different metals and design requirements. Below, we explore the major types of acid etching methods used for various materials and industries.
Steel Etching
For steel etching, a typical setup requires materials such as distilled water, acetone, a plastic container, rubber gloves, ferric chloride, wet-steel wool, etch resist, and dental paper. Proper preparation is essential for achieving precise, high-quality results.
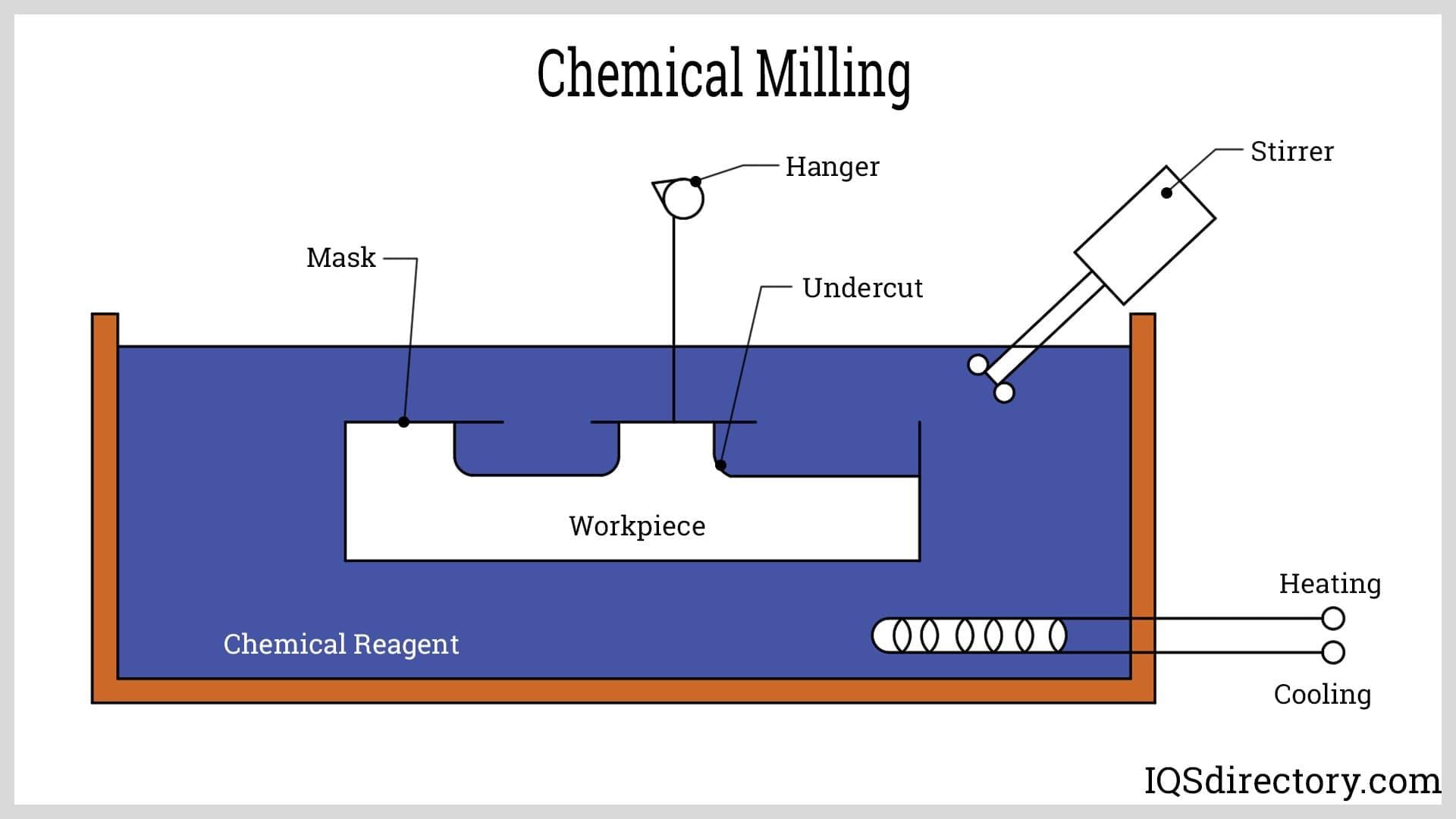
The process begins with the disassembly of the item to be etched (for example, a knife), ensuring no exposure of acid to sensitive parts such as liners, scales, or washers. After disassembly, the surface is meticulously cleaned with acetone to remove contaminants, allowing the etch resist to adhere firmly for crisp pattern definition.
An etch resist pattern is then applied, serving as a barrier that protects certain areas from acid exposure. Once the pattern is complete, the acid is prepared—typically ferric chloride diluted for safety and control—and the etching process commences in a well-ventilated environment.
Acid etching on steel can be performed via two primary techniques: acid bath etching (submerging the item) and focused etching (applying acid to targeted areas). After etching, post-processing steps such as sanding, stone washing, and thorough cleaning ensure a smooth, professional finish.
Why Choose Steel Acid Etching?
Steel etching is ideal for producing detailed logos, serial numbers, and intricate surface textures on tools, blades, and industrial parts. It offers unmatched accuracy and repeatability, making it popular in manufacturing, engineering, and custom knife-making.
Aluminum Etching
Aluminum acid etching stands out for its lower toxicity and safety compared to other metal etching processes. It is cost-effective and suitable for both industrial and artistic applications.
The process starts with preparing a mordant, commonly a copper sulfate and salt solution. After the copper sulfate dissolves, the solution must cool before use to prevent noxious fumes and ensure controlled etching. The result is a clean, sharply defined pattern with unique surface textures, especially when coarse salt is used.
Aluminum etching is favored in signage, electronics, automotive interiors, and decorative panel manufacturing. Its ability to handle fine details makes it the top choice for industries demanding lightweight and corrosion-resistant components.
Is Aluminum Etching Right for Your Project?
If you require lightweight, corrosion-resistant components with intricate detail, aluminum acid etching provides an efficient and affordable solution. Discover how aluminum etching can optimize your part production and surface design needs.
Other Metal Etching Processes
In addition to steel and aluminum, specialized acid etching techniques exist for copper, nickel, titanium, molybdenum, and various alloys. Each method involves unique process controls, etchant formulas, and masking techniques to achieve desired results. For instance, PCB manufacturing relies extensively on copper etching, while the aerospace sector prefers titanium etching for its strength and heat resistance.
Applications and Benefits of Acid Etching
Acid etching is a versatile fabrication technique with broad industrial, commercial, and artistic applications. Below, we highlight major uses and the distinct advantages that acid etching offers compared to alternative manufacturing methods.
Applications and Uses of Acid Etching
Where is acid etching most commonly used? Here are key industries and applications:
- Lead frames – Essential in semiconductor packaging, acid etched lead frames provide high-precision, reliable electrical interconnections.
- Electrical contacts and connectors – Etching enables the creation of intricate geometries for improved conductivity and compatibility in electronic devices.
- Motor laminations – Thin, precisely etched sheets minimize energy loss in electric motors and transformers.
- Medical devices and instruments – Stainless steel and titanium etching produces biocompatible parts with exacting tolerances, such as surgical tools and implant components.
- Plate heat exchangers – Acid etching forms complex channels for efficient heat transfer in HVAC, refrigeration, and process industries.
- Filters, meshes, and sieves – Fine, uniform openings achieved via etching are crucial for filtration, separation, and screening applications.
- Gaskets, washers, and shims – Precision-etched components are used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial equipment for sealing and spacing.
- Cranio maxillofacial implants – Custom, patient-specific implants are acid etched for superior fit and tissue integration in reconstructive surgery.
- Decorative panels and jewelry – Artists and designers use acid etching for detailed ornamentation on architectural metalwork and custom jewelry.
- Printed circuit boards (PCBs) – The electronics industry relies on copper acid etching to manufacture multilayer PCBs for computers, smartphones, and IoT devices.

Benefits of Acid Etching
Why choose acid etching over other metal fabrication methods such as stamping, laser cutting, or CNC machining? Consider these key benefits:
- No hard tooling required – Acid etching eliminates the need for expensive dies and molds, reducing setup costs and lead times for new designs.
- Unmatched design complexity – Photoresist masking and chemical etching enable the production of intricate features, micro-perforations, and complex geometries that are challenging or impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
- Cost-effective for prototyping and production – Rapid tooling changes and minimal setup cost make acid etching ideal for both high-volume production and low-volume prototyping.
- Short turnaround times – Fast design-to-production cycles allow for quick iterations and accelerated product development timelines.
- High accuracy and repeatability – Acid etching delivers tight tolerances and consistent results, ensuring each part meets exact specifications.
- Material properties remain unchanged – The process does not induce mechanical stress or heat distortion, preserving the original mechanical, chemical, and physical properties of the metal.
- Scalability – Suitable for both small batch runs and mass production without sacrificing quality or increasing per-unit costs.
- Clean edges and burr-free finishes – Unlike mechanical cutting, acid etching leaves smooth, burr-free edges, minimizing the need for secondary finishing operations.

Thinking about how acid etching compares to laser cutting or stamping for your next project? Explore our in-depth guides to metal fabrication methods to discover the right manufacturing process for your application.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Right Acid Etching Company
When sourcing acid etching services or looking for an experienced acid etching manufacturer, it’s essential to evaluate suppliers for quality, capability, and reliability. Making the right choice ensures your components meet demanding specifications and timelines. Here’s how to identify the best acid etching partner for your project:
- Industry experience – Choose companies with a proven track record in your specific industry, whether it’s electronics, medical devices, automotive, or aerospace.
- Technical capabilities – Confirm the supplier can handle your required materials, tolerances, part volumes, and finishing requirements.
- Certifications and quality systems – Look for ISO 9001, AS9100, or medical-grade certifications to ensure robust quality control.
- Design assistance – Top-tier manufacturers offer design for manufacturability (DFM) support to optimize your parts for acid etching.
- Lead times and scalability – Quick turnaround and scalable production capacity are vital for both prototyping and full production runs.
- Customer service and communication – Responsive service, clear communication, and flexible order management help keep your project on track.
Ready to compare acid etching suppliers? Use our curated list of Acid Etching Manufacturers to streamline your selection process. Each supplier profile details core expertise, material specialties, and process capabilities. Our platform also features direct contact forms for quote requests and an intuitive website previewer, allowing you to evaluate and shortlist vendors efficiently.
Not sure what questions to ask a potential acid etching partner? Consider:
- What materials and thicknesses do you routinely etch?
- What are your minimum and maximum part sizes?
- Can you assist with part design and prototyping?
- What is your standard lead time for prototypes and production orders?
- Do you offer additional finishing or assembly services?
- What quality certifications do you maintain?
- How do you ensure on-time delivery and consistent quality?
For a seamless supplier evaluation, compare at least 4 to 5 acid etching companies using our comprehensive directory. Review their websites, customer testimonials, and showcased projects to gauge their strengths. Then, submit your RFQ to multiple suppliers with a single message to receive competitive quotes and personalized recommendations.
Want to learn more about acid etching solutions for your industry? Browse our expert resources, case studies, and application guides to discover how acid etching can enhance your product’s performance, appearance, and value.






 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting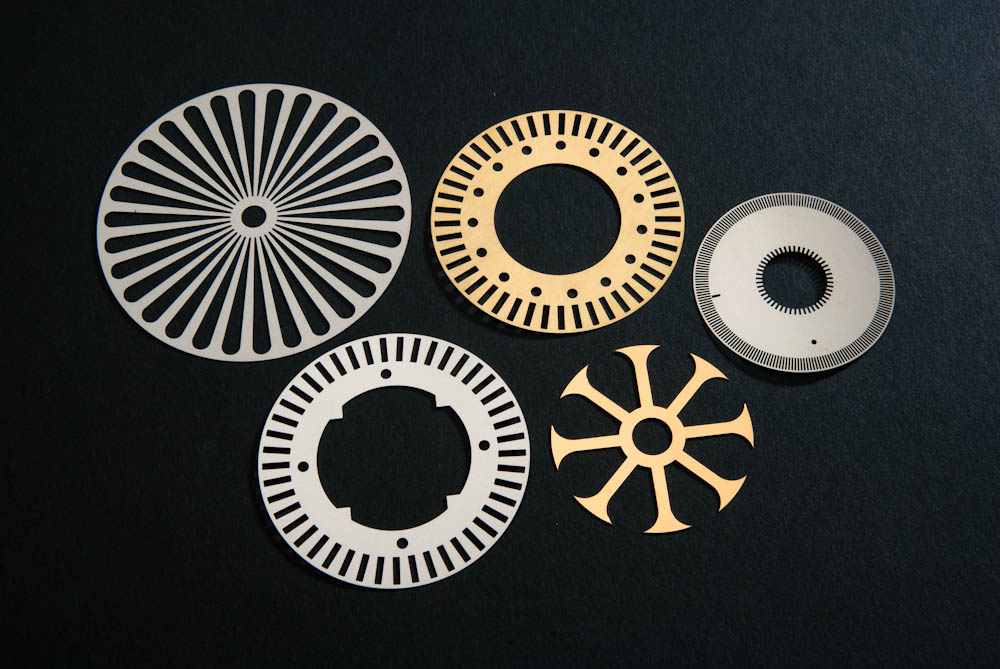 Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication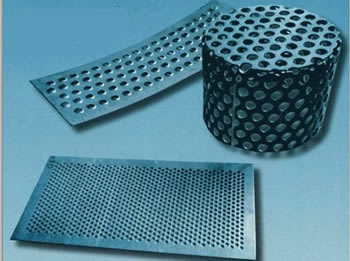 Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services